Spring Boot and Postgres Using Docker Compose
In this blog post, we will walk through the steps to run a Spring Boot application and PostgreSQL database in Docker using Docker Compose.
Prerequisites
Before we start, make sure you have the following installed on your machine:
- Docker
- Docker Compose
- Java Development Kit (JDK)
- Maven
Step 1: Create a Spring Boot Application
Before we start, we need a spring boot application for this tutorial. For this, you can go to Spring Initializer and generate a project based on your needs.
This will create a new Spring Boot project with a basic structure. Open the pom.xml file and add the following dependencies:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<version>42.3.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)This will add the PostgreSQL dependencies to our project.
Next, create a new class named UserController.
package com.example.docker_spring_boot_postgres;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<String> getUsers() {
String query = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM users";
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(query, Integer.class);
return new ResponseEntity<>("Total users: " + count, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}Code language: Java (java)This class contains a simple GET endpoint that returns the total number of users in the database. We will create the database schema in the next step.
Step 2: Configure PostgreSQL
We need to configure our Spring Boot application to connect to a PostgreSQL database. Open the application.properties file located in src/main/resources and add the following configuration:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://postgres:5432/dockerdb
spring.datasource.username=dockeruser
spring.datasource.password=dockerpassword
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.DriverCode language: Properties (properties)This will configure our application to connect to a PostgreSQL database named dockerdb with the username dockeruser and password dockerpassword.
Step 3: Create a Dockerfile
We need to create a Dockerfile that will build an image of our Spring Boot application. Create a new file named Dockerfile in the root directory of the project and add the following content:
FROM openjdk:11-jre-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY target/docker-spring-boot-postgres-1.0.0.jar .
EXPOSE 8080
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","docker-spring-boot-postgres-1.0.0.jar"]
Code language: Dockerfile (dockerfile)My apologies. Let me continue with the next steps.
Step 4: Create a Docker Compose File
We need to create a Docker Compose file that will define the services required to run our application. Create a new file named docker-compose.yml in the root directory of the project and add the following content:
version: '3.8'
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:13-alpine
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: dockeruser
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: dockerpassword
POSTGRES_DB: dockerdb
ports:
- "5432:5432"
volumes:
- postgres-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
app:
build: .
ports:
- "8080:8080"
depends_on:
- postgres
environment:
SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL: jdbc:postgresql://postgres:5432/dockerdb
SPRING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME: dockeruser
SPRING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD: dockerpassword
volumes:
postgres-data:Code language: YAML (yaml)This file defines two services: postgres and app. The postgres service uses the official PostgreSQL image and creates a volume to persist the data. The app service uses the Dockerfile we created earlier to build an image of our Spring Boot application. It also defines environment variables to configure the database connection.
Step 5: Build and Run the Application
Now that we have created the Dockerfile and Docker Compose file, we can build and run the application using Docker Compose. Open your terminal and run the following command in the root directory of the project:
$ docker-compose up --buildThis command will build the Docker image for our Spring Boot application and start the PostgreSQL and application containers. Once the containers are running, you should be able to access the application at http://localhost:8080/users
Also in the list of containers, you should be able to see the database and application containers.
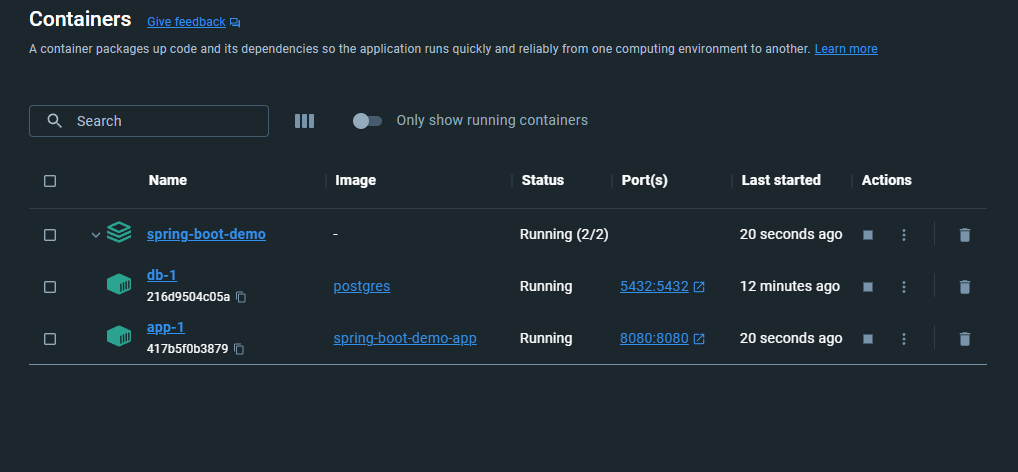
Conclusion
In this blog post, we walked through the steps to run a Spring Boot application and PostgreSQL database in Docker using Docker Compose. Docker Compose provides an easy way to define and manage multi-container applications. By using Docker, we can create a consistent and reproducible runtime environment, making it easier to develop and deploy applications.
hi, before docker compose up we need to build the java project right. but when i build then it failed because u specified in yml fule the datasource url.it not found.how to do so
it may be the case that you are not passing the environment variables as I do in the example. In worst case, You could do something like the below.
And then, you could mount your local application.properties to the above config location like below.
app: build: . ports: - "8080:8080" depends_on: - postgres volumes: - ./local/path/to/app.properties:/app/conf/application.properties